With more than a decade-long head start, one would have thought vitamin D would have cured cancer by now, if not Covid-19. There are over 10,000 reports about vitamin D supplementation published in the past 10 years, posted at the National Library of Medicine.
But all is not rosy in vitamin-D Land. Speaking out of two sides of their mouths, researchers say vitamin D does/doesn’t work; say over a billion people on earth are vitamin D deficient, but also say they the public is wasting money on sunshine pills.
Which is it? A wonder cure, or the biggest disappoint in nutritional medicine?
The answer is, it will be what modern medicine chooses it to be, because the delivery of medicine today is on the medical industry’s terms, not determined by public needs or demands.
Like mafia, the medical industry has to get a cut of the pie, or it will malign and disqualify whatever threatens its income. As a dietary supplement, the public’s direct access to vitamin D without doctoring is a problem for modern medicine because of vitamin D’s broad ability to quell many diseases. The biggest confounding factor in vitamin D science is the medical profession itself.
When did the vitamin D revolution begin?
The vitamin D revolution was signaled by leading researchers over a decade ago. Drs. Cedric and Frank Garland who connected vitamin D deficiency to cancer with their ground breaking report published in 1980 and Dr. Michael F. Holick who wrote about the “vitamin D pandemic;” and Bruce W. Hollis PhD who contributed to the science of blood testing, were the researchers who led the way.
Called the “nutrient of the decade” in 2010 by Ronald Hoffman MD, former president of the American College for Advancement in Medicine, this vitamin/hormone came out of the research closet to offer far more health benefits than its widely advertised ability to utilize calcium for bone growth and prevent rickets in growing children. Vitamin D’s greatest promise is its central role in the immune system and should be front and center in infectious disease and cancer prevention.
Living in the dark
How could such a widespread deficiency plague modern man when it is free, not confined to dietary or supplemental sources, and all that is required to be vitamin D sufficient is to walk outside in midday sun, at least in southern latitudes.
Essential for human life, the vitamin D tank must never be empty. Months of it are literally stored in the liver in summer months to get through winter. A mega-dose of injectable vitamin D maintains elevated blood levels for 84 days. Older women often have 300,000 units of vitamin D injected for wintertime bone protection without side effect. Even large single oral doses up to 300,000 units are safe and effective.
Safe upper limit
It is inconceivable that a 4000-unit vitamin D pill (the so-called safe upper intake limit) could be problematic beyond that point. 4000 international units (IU) is just 1/10th of a milligram (100 micrograms). This preposterous safety limit point exposes the sun/vitamin D phobia that now prevails in modern medicine. (More about this below.)
The costs
Vitamin D inadequacy costs ~$40-50 billion a year (2004 data) whereas sun-related diseases (skin cancer) costs ~$6-7 billion a year in the US. Modern medicine knows, if vitamin D adequacy could be achieved by the entire population, $40-50 billion in insurance reimbursements to doctors and hospitals would be taken out of its pockets. The medical industry recognizes the vitamin D revolution can’t be stopped, but it can stall for time.
How much supplemental vitamin D are Americans taking?
WebMD provides usage data: In 1999-2000, 0.3 percent of U.S. adults took 1,000 IUs or more of vitamin D daily. By 2013-2014, slightly more than 18 percent of adults were taking that much vitamin D daily.
In 2007-2008, 0.2 percent of Americans took 4,000 IUs or more daily. By 2013-2014, that number was 3.2 percent.
Demand for D supplements soar
Vitamin D’s real promise has yet to be realized for a great portion of human populations, even though the demand for this vitamin as a dietary supplement has grown from $30 million in 2008 to over $770 in the US annually (2021), and projected to reach $1.6 billion globally by 2025.
$770 billion divided by a population of 328 million Americans amounts to just $2.34 per year per capita. The tab for 200 million Americans taking a $10/month vitamin D pill would amount to $2.4 billion, showing the market potential for this supplement.
Why wait for symptoms of D-deficiency to arise and then inappropriately treat the symptoms with anti-inflammatory, anti-germicidal and anti-depressant drugs? That is the common practice today. Given there are more than 100 types of autoimmune diseases, and vitamin D normalizes body-against-itself autoimmunity, suggests a large number of health benefits can accrue from making vitamin D a new paradigm in modern medicine.
Typical blood concentrations by dose
What are the typical blood concentrations achieved by supplementation?
For reference, there are two ways to measure blood levels of vitamin D: nanograms per milliliter and nanomoles per liter.
1000 IU: 12.4 nanograms/milliliter/ nanomole per liter
Vitamin D-deficiency is defined as below
20 nanograms/milliliter or 50 nanomoles/liter blood sample
5000 IU: 27.8 nanograms/milliliter/ 69 nanomoles per liter
10,000 IU: 48.1 nanograms/milliliter/ 24,960 nanomole per liter
That makes 1000-4000 mg vitamin D pills almost worthless, save for sunshine that prevents abject deficiency.
Canadian researcher Reinhold Vieth showed a 400 IU/day dose for several months achieves little or no detectable effect on the circulating concentration of vitamin D. Embarrassingly, that is the amount of vitamin D in fortified milk for many years – a useless dose.
What percentage of US population is D-deficient?
A 2011 report published in Nutrition Research estimated Vitamin D deficiency (defined blood serum concentrations below ≤20 nanograms/milliliter/50 nanomoles/liter) was 41.6%, with the highest rate seen in blacks (82.1%), followed by Hispanics (69.2%).
In winter, every American living above the 37th parallel except vitamin D-supplement users is probably vitamin D-deficient.
Why not food fortification?
What about fortifying foods? The World Health Organization (WHO) says food fortification is supposed to kick in “to provide most (97.5%) of the individuals in the population group(s) at greatest risk of deficiency with an adequate intake of specific micronutrients, without causing a risk of excessive intakes in this or other groups.”
Therefore, when 2.5% of the population has blood levels below 10-12 nanograms per milliliter/ 25-30 nanomole/liter blood sample, food fortification should be implemented. Milk is fortified with 400 units of vitamin D for growing children who need vitamin D. Obviously, food fortification isn’t working.
Provision of vitamin D from the diet is insignificant
Using data from a 2009-2012 study, the dietary intake of vitamin D below the Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) was 100%! About 80% of vitamin D comes from solar UV-B radiation and about 20% comes from the diet. Thank God for sunlight.
Public health authorities recommend a miniscule 400-800 IU (10-20 micrograms) of vitamin D to achieve blood levels in the range of 25-50 nanomole/liter or 10-20 nanograms/milliliter blood sample. If every American achieved this blood level, they would all be on the border of deficiency, especially if living in northern climates where the effects of the tilting of the earth away from the sun during winter months reduces solar radiation and natural production of vitamin D.
These numbers appear to be ridiculously low when compared to sunlight exposure. Just 10 minutes in midday sun without sunscreen with skin exposed will generate ~10,000 units of vitamin D (1000 units per minute)! So, the 400-800 IU recommendation for food fortification equals less than a minute of sunshine. That is absurd!
The Food & Nutrition Board established the safe upper limit for vitamin D at 4000 IU (100 micrograms) per day, which is equivalent to 4 minutes of sunshine. That is also absurd. Have you ever heard of anybody developing vitamin D toxicity from going out in the sun for more than 4 minutes?
I hope readers are following along here how modern medicine is about as fearful of sunlight as Count Dracula.
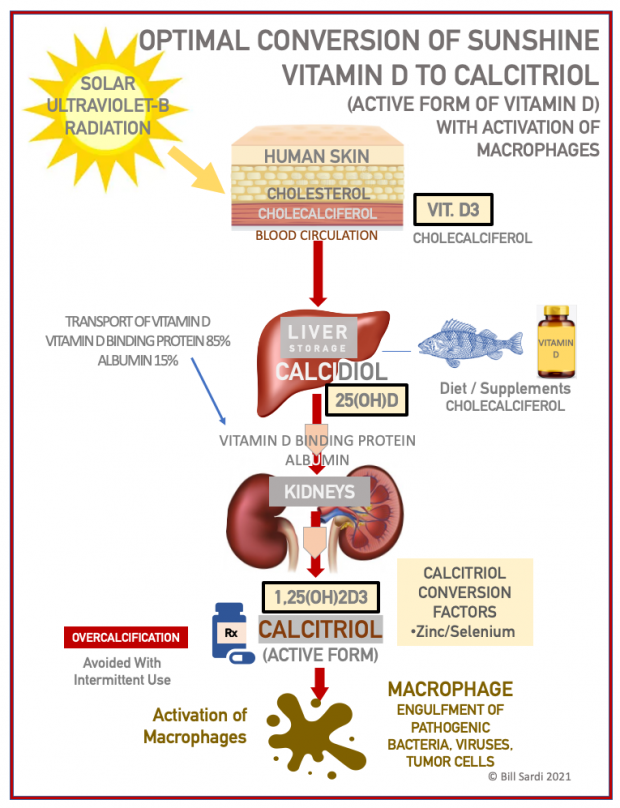
Understanding vitamin D metabolism
According to Dr. Bruce Hollis, affiliated with the Medical University of South Carolina:
The circulating half-life of the intermediate form of vitamin D (calcidiol) is many weeks; for vitamin D3 it is 1 day; and for activated vitamin D (calcitriol) it is a few hours. Vitamin D is eventually excreted in bile, feces and urine. Therefore, the only known way to maintain constant vitamin D blood levels is daily supplementation or skin/sun exposure to solar UV rays.
Even a 100,000-unit dose of vitamin D is cleared from the blood circulation within a week, making vitamin D basically undetectable (though some is stored in the liver). Thus, the only known way to sustain constant circulating vitamin D concentrations is by daily supplementation and/or chronic UV exposure.
A 400 IU/day dose for several months will achieve little or no detectable effect on the circulating concentration of vitamin. D However, if one supplements for extended periods with 2000–6000 IU/d vitamin D3, stable circulating concentrations of vitamin D are maintained in the range of 10–40 nanograms/milliliter. Dosing of 400, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/day; 28 000 IU/week; 120 000 IU/month; 360,000 IU every 3–4 months will maintain vitamin E levels without over-calcification.
Daily doses of vitamin D result in stable circulating concentrations of both D3 and intermediate calcidiol, whereas weekly or longer interval dosing will result in large fluctuations in circulating vitamin D but stable concentrations of calcidiol in the liver, the intermediate form of vitamin D. Nursing mothers need 6000 IU/day of vitamin D3.
Plethora of vitamin D studies with declaration of pandemic
The Covid-19 pandemic produced a plethora of vitamin studies in a short time. With no vaccines in place, the Covid-19 pandemic took second-tier treatments like vitamins and thrust them to the front of the battle to save human lives from a mutated virus that no human had immunity from. Vitamin D/Covid-19 studies were initially positive:
· An oral bolus of 80,000 IU of vitamin D3 prior to a Covid-19 diagnosis lowered the mortality rate.
· When middle-age adults who tested positive for Covid-19 were given 60,000 IU of vitamin D3 daily for 7 days or an inactive placebo pill, more than 60% tested negative within 21 days compared to 20.8% showed negative in the placebo group.
· According to one study, Covid-19 patients tend to have pre-infection vitamin D deficiency, defined as less than 20 nanograms/milliliter blood sample. Covid-19 patients were (14.3 times increased risk to be vitamin D deficient and 2.031 times more likely to have diabetes, and these patients had higher rates of mortality and co-morbidities.
· Another interesting observation is that solar UV radiation correlates with reduced severity of Covid-19 infection and low incidence of Covid-19 infection altogether. If the timing of vaccination correlates with the summer increase in UV radiation, that will make the Covid-19 vaccines falsely appear to be more effective.
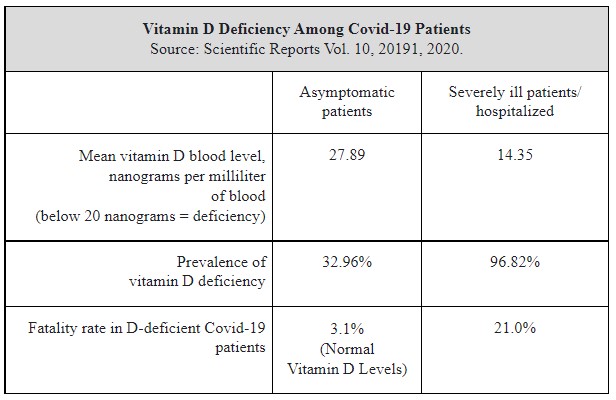
· A revealing study of Covid-19 patients was undertaken. Covid-19 patients without symptoms (asymptomatic) vs severely ill patients in hospital. Here are the results of that study:
Vitamin D studies fizzled
But then vitamin D supplementation fell into disrepute. The mistaken presumption is those who are vitamin D-deficient will benefit from supplementation. But that isn’t always the case.
Apart from Covid-19, rigorous vitamin D studies didn’t find any health benefit. A landmark study published in 2018 found vitamin D supplementation did NOT boost bone mineral density and prevent falls and hip fractures. But of course, among post-menopausal females who are prone to fractures, another hormone, estrogen, is responsible for maintaining bone density. Same goes for testosterone for males. Conclusion: researchers were putting the wrong hormone to the test.
In another example, a study published in 2019 in the New England Journal of Medicine did not result in a lower incidence of invasive cancer or cardiovascular events compared to an inactive placebo. However, a significant reduction in colon cancer risk was shown for free-unbound vitamin D, which is addressed later in this report.
Other studies revealed vitamin D levels unexpectedly correlated with an increase falls and fractures among older women. A review of 137 diseases concluded any claim vitamin D is associated with reduced disease incidence is spurious. Vitamin D deficiency was called a “pseudo disease,” and vitamin D pills as an “imposter” substitute for sunshine.
Then came the Covid19 pandemic and contrary studies:
· Vitamin D supplementation among Covid-19 patients was found to be inconclusive and may be skewed by unknown confounding factors.
· Even when a single high-dose of vitamin D3 was administered (200,000 IU) there was no effect on days of hospitalization. However, other studies came to a different conclusion and recommended vitamin D supplementation for Covid-19. Why?
· Of interest is a study where 42% of Covid-19 patients were vitamin D deficient blood levels (below 20 nanograms/milliliter of blood sample) and the odds of infection were 3.3 times greater among those with D deficiency. However, there was no significant association between vitamin D status and mortality. Another study found the same thing, that vitamin D deficiency decreased the risk for severe Covid-19 disease but not a fatal outcome.
· Researchers went further in their investigation and employed genetic screening to determine if inherited factors predisposed individuals for higher or lower vitamin D blood levels and increased or decreased risk for Covid-19 infection and mortality. There was no association between genetically-predicted vitamin D levels and Covid-19 susceptibility. However, the study in question did not include vitamin D-deficient individuals.
Despite the negative studies, 80% of Covid-19 patients are vitamin D deficient.
Investigation into vitamin D as a nutrient to prevent, treat and even cure Covid-19 reveals voluminous evidence a deficiency of the active form of this sunshine hormone/vitamin (calcitriol) is responsible for an estimated 87% of Covid-19 deaths.
Don’t blame failed studies on vitamin D
There are known reasons why vitamin D doesn’t work.
· Obesity is another factor that reduces vitamin D blood levels. Obese adults need 2 to 3 times more vitamin D than lean adults to treat vitamin D deficiency. Body weight per day could explain 34.5% of variation in circulating vitamin D.
There is far greater incident cancer reduction among normal-weight adults than obese adults when taking vitamin D. In the US obese Covid-19 patients are 1.8 to 3.6 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU. In China, 88% of deceased Covid-19 patients were overweight.
· One study shows nearly 80% of patients with chronic kidney disease have low vitamin D levels. As readers learn here, the kidneys are where the final step of vitamin D metabolism occurs, where calcidiol is converted to the active form of vitamin D, calcitriol. I in 3 diabetics have kidney disease.
· Chronic alcohol intake reduces circulating vitamin D and impairs immunity.
· Serum vitamin D levels are lower among women with autoimmune hypothyroidism. Of note, a deficiency of the trace mineral zinc impairs thyroid hormone levels.
More than meets the eyes
There is lot more to vitamin D than meets the eye. Excessive vitamin D could result in over-calcification, so the body makes vitamin D in the skin upon exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation, stores it in the liver that keeps a few months supply to get through winter, then converts it to its active form (calcitriol). Vitamin D in the blood is predominantly the bound form, with only ~1% being unbound and bioavailable.
The crux of vitamin D metabolism is it must be metabolized in the kidneys to its active form, calcitriol.
What is the bottom-line delivery of vitamin D to our body?
The human body limits the amount of vitamin D available for nutriture so as to prevent over-calcification, vitamin D being the regulator of calcium availability. So, vitamin D3 is synthesized in the skin, shuttled to the liver for storage (as calcidiol) and released on an as-needed basis, being transported via the vitamin D binding protein to the kidneys, where it is enzymatically metabolized into the active form of vitamin D (calcitriol).
Some 85-90% of vitamin D (calcidiol) released from the liver is bound to the vitamin D binding protein and 10-15% is bound to albumin, so less than 1% is the active unbound (free) vitamin D (calcitriol).
The disconnect is that customarily blood laboratories only measure how much unmetabolized vitamin D3 is in circulation in the bloodstream, not how much active vitamin D (calcitriol) is available. Advances in testing now make it possible to measure activated (free, unbound) vitamin D.
While some studies show free-unbound vitamin D levels are not lower in critically ill patients versus healthy patients, the mistaken presumption is that critically ill patients vitamin D needs are the same as ill patients. While it was found that vitamin D-deficient men have a two-fold increase mortality risk, the free-D fraction was unrelated to mortality. However, there is no reason to dismiss vitamin D outright as modern medicine has done. Free-unbound vitamin D correlates better with bone density than standard measurements of vitamin D3.
400 units a day doesn’t raise blood levels
Vieth and colleagues demonstrated that the 2000 IU/day upper safe limit for vitamin D assigned by the Institute of Medicine in 1997 was incorrect and that daily intakes of vitamin D up to 4000 IU/d were indeed safe.
To make matters worse, a statistical error mis-estimated the safe upper tolerable daily intake. In a report entitled “The Big Vitamin D Mistake,” the corrected daily intake for adults is 8000 IU per day.
The foot-dragging by modern medicine is very apparent here.
Zero mortality!
An important finding is that vitamin D3 is a predictor rather than just a side effect of infection. Raising serum vitamin D levels above 50 nanograms/milliliter to prevent new Covid-19 outbreaks produces a theoretical point of zero mortality at this blood level!
There is strong evidence that low D3 is a predictor rather than just a side effect of the infection. DESPITE ONGOING VACCINATIONS (author emphasis), researchers in Germany recommend raising serum intermediate D (calcidiol) levels to above 50 nanograms/milliliter blood sample to prevent or mitigate new Covid-19 outbreaks due to escape mutations or decreasing antibody activity. In other words, don’t just rely upon vaccination to achieve immunity.
The case for calcitriol, metabolized in the kidneys
In an attempt to resolve the equivocal evidence to substantiate the use of supplemental vitamin D, researchers postulated that vitamin D was not converted to calcitriol, which would explain the null studies.
Calcitriol was put to the test. Two groups of 25 hospitalized patients were given calcitriol or no treatment. The length of stay in the hospital was 9.2 days vs 5.5 days for the calcitriol group. A significant reduction in oxygen requirements in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 was demonstrated. There were 3 deaths in the no-treatment group and zero deaths in the calcitriol group.
This would suggest lack of conversion from calcidiol to calcitriol in the kidneys among Covid-19 patients.
In the Catalonia region of Spain calcitriol was employed among 8,076 patients with kidney disease. Calcitriol reduced risk for Covid-19 infection by 22% and mortality by 43%.
Foot dragging
Calcitriol is a largely underutilize and under-prescribed drug. Oncologist Donald L. Trump (not related to former US President), affiliated with the Inova Healthcare in Virginia, writes a seminal paper about the missed opportunity of calcitriol therapy in a 2018 report. The context of his report is cancer.
Dr. Trump notes that literally hundreds of vitamin D drug analogues (similar molecules) have been developed in a futile attempt to overcome hypercalcemia associated with the use of calcitriol, its only known side effect. Calcitriol’s drawback, moderate, mild, transient hyper-calcification, can be overcome by intermittent use, says Dr. Trump.
In other words, the research community chose to develop patentable forms of calcitriol given the contrived fear of over-calcification and the desire to get-rich.
Zinc: how to convert vitamin D to its active form
The masses don’t need to get a prescription for calcitriol from their doctor. The trace mineral zinc facilitates maximum calcitriol levels via release from white blood cells known as macrophages. Zinc is particularly important when calcium or phosphorus are depleted. Zinc is commonly deficient among patients with kidney disease. The lack of stomach acid in senior adults impairs zinc absorption. Selenium is needed to release free unbound zinc from its carrier protein, metallothionein.
It is unconscionable that oncologists and infectious disease specialists don’t prescribe zinc across the board for their patients given its important role in releasing calcitriol from its binders.
Zinc is also documented to increase vitamin D receptor on the surface of cells and thus increase calcium binding protein.
Furthermore, the trace mineral zinc inhibits nagalase, the enzyme that degrades a liver protein called Gc Protein Macrophage Activating Factor (GcMAF). It is GcMAF that stimulates white blood cell called macrophages that literally engulfs and devours pathogens and cancer cells.
Bottom line
Well, there you have it. Theoretically vitamin D supplementation could have brought the Covid-19 death rate to zero. And who knows how many cases of cancer would have been altogether prevented or treated to effect a cure (there being no sure-cures for cancer in the last 50 years of cancer research).
In 2008 it was reported that just 1,100 IU per day of vitamin D3 combined with 1,400-1,500 milligrams of calcium reduced the risk for all-cancer incidence by 77%! That study was predictably dismissed by a sole flawed critique.
Daily dosing
Dose and frequency also predict effectiveness.
Daily oral dosing results in a greater reduction in cancer mortality than infrequent bolus injections. Daily 4000-6000 IU vitamin D3 to achieve a 60 nanogram/milliliter blood concentration of the intermediate form of vitamin D (calcidiol) reduces the risk for breast cancer by 80%. Yet modern medicine remains unconvinced. Even just 2000 IU vitamin D3 supplementation reduces all-cancer risk.
Adults who maintain the highest blood levels of vitamin D are half as likely to die from any cause compared to people who have the lowest vitamin D levels over a 7-year period. Raising levels of active vitamin D (25(OH)D3 or calcitriol) to 40-60 nanograms/milliliter blood sample reduces the risk of many cancers.
Modern medicine ushered in sun avoidance practices since 1980 that actually increased cancer risk. Vitamin D or the lack thereof explains geographical, racial (skin pigmentation), socio-economic and age-related cancer factors.
And in what amounted to a secondary pandemic, we learn mental depression during the Covid-19 lockdown soared from 11% to 42%, and that downing vitamin D pills during the sunless planetary Covid-19 lockdown of human populations could have prevented or resolved needless cases of mental depression (un-seasonal-affective disorder).
Take home advice:
· Are you getting daily midday sunshine? You can’t possibly overdose on sunshine vitamin D.
· Are you supplementing with 8000 IU of vitamin D per day?
· Are you supplementing your diet with zinc and selenium to activate vitamin D?
There is more to this vitamin D story than has been written here. New developments in vitamin D metabolism are underway. Standby.