By Dr. Mercola
New research has emerged linking low vitamin D levels with a risk of cognitive decline and mental impairment, according to studies conducted on elderly Chinese.
Duke-NUS (a collaboration between Duke University in North Carolina and the National University of Singapore)1 announced the deficiency is caused primarily by lack of exposure to sunlight, which scientists already knew humans require to maintain strong bones and healthy muscles.
The new research has now broadened to encompass vitamin D as necessary for optimal brain function.
European and North American studies that have associated low “D” levels with cognitive decline further support previously noted heart and neurodegenerative diseases in individuals with the same deficiency. News-Medical observed:
 NOW Supplements, Vitam...
Buy New $9.92 ($0.04 / Count)
(as of 04:43 UTC - Details)
NOW Supplements, Vitam...
Buy New $9.92 ($0.04 / Count)
(as of 04:43 UTC - Details)
“Regardless of gender and extent of advanced age, individuals with lower vitamin D levels at the start of the study were approximately twice as likely to exhibit significant cognitive decline over time.
In addition, low vitamin D levels at baseline also increased the risk of future cognitive impairment by [two to three] times.”2
Researchers concluded that the findings reinforced theory that vitamin D protects against neuron damage and loss.
They anticipate further reviews on the mechanisms vitamin D exerts in protecting neurons and how optimizing vitamin D levels may curtail the rapidly increasing number of aging individuals suffering from cognitive decline.
Scandinavia Is Not the Only Place With Low Vitamin D Levels
Elle UK reported that Brits ingest an average of 3 micrograms (120 IU) of vitamin D in food and receive low levels of year-round sunlight, which puts them at greater risk for bone-related diseases.
“Women in particular should take note — history shows our bones degrade faster than our male counterparts.
When we hit menopause, the loss of bone density accelerates rapidly (up to 20 [percent] in just [seven] years), so keeping vitamin D levels topped up can only help to hedge our bets against calcium deficiency and irreversible bone loss later in life.”3
Residents of the British Isles have long noticed that sun is a relatively rare commodity. That’s why Public Health England (PHE)4 issued a report recommending that its inhabitants take vitamin D supplements, whereas only “at risk” individuals and children under 5 were previously given this recommendation.
Instant Access to Current Spot Prices & Interactive Charts
PHE suggested 10 micrograms (400 IU) daily, which is still far below the amount most people need to stay healthy. Online British newspaper Health Spectator noted:
“When the sun goes into hiding, it’s difficult to achieve that through food alone. Why do we need vitamin D? Well, it regulates the calcium and phosphate in the body, making it vital for bone, muscle and tooth development and growth.
A lack of it can lead to a higher risk of bone disease and fracture and, in the worst cases, rickets. There are also studies that suggest vitamin D can help the battle against cancers, cardiovascular disease and multiple sclerosis.” 5
In mid-December 2015, Scandinavians in Oslo basked in sun for only six hours and four minutes, between the hours of 9:08 a.m. and 3:12 p.m. Edinburgh, Scotland, got an hour more than that, so authorities in that area of the world are well aware of the need for vitamin D.
Norway Devises Plan to Reflect Sunlight on Residents
Norway’s Food Safety Authority even upped the recommendation to 20 micrograms (800 IU) per day in 2013 and advised people not to neglect sun exposure, and to supplement with foods high in vitamin D, such as cod liver oil and other oily fish.
 Life Extension Super K...
Buy New $18.24 ($10.36 / oz)
(as of 02:00 UTC - Details)
Life Extension Super K...
Buy New $18.24 ($10.36 / oz)
(as of 02:00 UTC - Details)
Even the Vikings understood the importance of this practice, and reportedly rubbed cod liver oil into their skin for muscle pain and consumed whole cod livers dipped in cod liver oil for a double whammy.
The town of Rjukan, Norway, devised an ingenious plan to literally reflect sunlight on its residents. The town, shadowed by mountains for six months of the year, installed three gigantic mirrors on the mountains to bring not just the reflection of the sun but also its warmth. As The Guardian enlightened:
“Helicoptered in and installed 450m [1,312 feet] above the town square, the 5m [16.4 feet] kroner (£520,000 [$694,000]) computer-controlled mirrors, or heliostats, are more commonly used to create solar power in sun-drenched regions of the Middle East.
Here, the solar energy the heliostats capture is used to power their tilting trajectory as they follow the sun’s brief dash across the Norwegian winter sky.”6
People of the town can also catch a cable car and zip to the mountaintop for their sun connection.
Sunscreen Versus the Vital Need for Vitamin D
Although the horror stories of excess sun and subsequent skin cancer have scared most Americans and Brits into the shadows, Louis Levy, head of nutrition science at Public Health England, told BBC Radio that people using sunscreen as recommended will not get enough vitamin D.
“This is a change in advice, previously we have said that babies from [6] months to [5] years should have a supplement and only those people at risk of deficiency should take a supplement.
Previously we felt that everybody would get enough from the sunlight. This is new advice based on evidence looked at over the last five years. When you go out, you do need to have short bursts without sunscreen and make sure that you don’t get sunburnt.”7
In America, even the National Institutes of Health (NIH) admits that sunscreens block vital vitamin D-producing sunrays, and suggests that a little sun without sunscreen is good. On its webpage, the NIH says:
” … [A]pproximately [five to] 30 minutes of sun exposure between 10 [a.m.] and 3 [p.m.] at least twice a week to the face, arms, legs, or back without sunscreen usually lead to sufficient vitamin D synthesis.”
What Does Vitamin D Deficiency Look Like?
With the absence of a sunny vista, distressingly low vitamin D levels can be manifested in several ways.
SAD Syndrome, aka seasonal affective disorder, is a type of depression related to changes in seasons, thought to be related to the lack of sunlight. Between 60 percent and 90 percent of sufferers are women between the ages of 15 and 55. Psych Central describes it perfectly:
 Nivagen Pharmaceutical...
Buy New $17.05
(as of 11:55 UTC - Details)
Nivagen Pharmaceutical...
Buy New $17.05
(as of 11:55 UTC - Details)
“While some perceive winter as a festive time when their worlds are blanketed by the purity of snow, others feel that they are being suffocated by a literally colorless existence.”8
Science reveals that when people are exposed to sunlight, their mood automatically elevates due to the brain hormone serotonin. Researchers examined the effects of vitamin D on the relative cheerfulness of 80 elderly patients and found the ones with the lowest vitamin D levels were 11 times more prone to depression.9
Additionally, older adults are more inclined to stay indoors, so they get less sun exposure. People over the age of 50 also don’t produce vitamin D as easily by metabolizing sunlight, and their kidneys don’t convert vitamin D into a form their body can use quite as quickly.
African Americans and others with darker skin are even more prone to a vitamin D deficiency because it takes 10 times more sun exposure to generate the same amount as in someone with pale skin. That’s because the more pigment you have, the more sunlight you need to get adequate “D” levels.
People with higher body weight or muscle mass also require more vitamin D than people with slighter statures because vitamin D is fat soluble — your body acts like a “sink” and collects it.
You may also experience gastrointestinal problems that inhibit the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, as in gut disorders such as celiac and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Not Enough Vitamin D Versus Too Much
Official estimates of deficiency in this vitamin in England are 1 in 5 adults and 1 in 6 children. According to BBC News, vitamin D is important because:
“Its main function is to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body, which are vital for the growth and maintenance of healthy bones, teeth and muscles. In extreme cases, low levels can lead to rickets in children — where the bones become soft and weak and misshapen as they continue to grow.
In adults, vitamin D deficiency can lead to osteomalacia — causing severe bone pain and muscle aches. But there is a balance — too much vitamin D can lead to high levels of calcium in the blood which can cause heart and kidney problems.”10
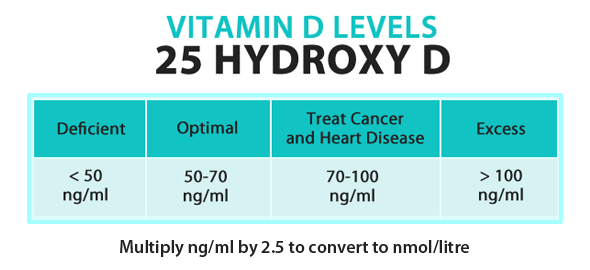
In the U.S. it is estimated that as much as 41.6 percent of the general population could be vitamin D deficient, when defining deficiency as a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration of less than 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L). When looking at specific populations such as blacks and Hispanics, the numbers may be as high as 82.1 percent and 69.2 percent, respectively.11
How do you know if you have enough vitamin D? One approach to determining optimum vitamin D levels is to look at the current recommendation for nursing mothers, says professor and endocrinologist Dr. Robert Heaney, who founded Creighton University’s Osteoporosis Research Center, which focuses on bone biology.
“Very recent work coming out of the Medical University of South Carolina has shown definitively that such a woman needs 6,000 international units (IU) of vitamin D per day, every day, in order for her infant to be adequately nourished, at least as far as vitamin D is concerned.”
Nature Bright SunTouch... Buy New $68.99 (as of 10:45 UTC - Details)
How Much Vitamin D Is Ideal?
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) recommends 20 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) of serum concentration of 25-hydroxy vitamin D as an adequate level, or 600 IUs a day up to age 70 and 800 IUs if you’re over 70, but many vitamin D researchers believe that’s not even enough to prevent osteomalacia, let alone take advantage of vitamin D’s additional health benefits.
Fortunately, vitamin D supplements are readily available, but due to government nutrition recommendations for children and the elderly, only informed choices will help people stay on track with the vitamin D levels that will offer optimal health. If you can’t get enough sunshine for whatever reason, then you can take a vitamin D3 supplement.
As a general guideline, research by GrassrootsHealth suggests adults need about 8,000 IUs per day to achieve a serum level of 40 ng/ml. If you do opt for a vitamin D supplement, please remember that you also need to boost your intake of vitamin K2through food and/or a supplement, as well as get your levels tested to be sure you’re safely within the therapeutic range.
Vitamin D in Food
Foods containing vitamin D and their recommended dietary allowance (RDA), according to the George Mateljan Foundation,12 a not-for-profit food and nutrition science organization, include:
•Four ounces of wild-caught Alaskan sockeye salmon — 128 percent of the RDA
•3.2 ounces of sardines — 44 percent of the RDA
•One egg — 11 percent of the RDA
•Shiitake mushrooms — 5 percent of the RDA
Keep in mind that the RDA is far lower than necessary to raise your vitamin D levels into the therapeutic range, so it’s difficult to achieve enough vitamin D from dietary sources alone. In addition, it’s ideal to get your vitamin D from sunlight because the sun offers a wealth of health benefits above and beyond vitamin D.
The Role of Vitamin D in Disease Prevention
A growing body of evidence shows that vitamin D plays a crucial role in disease prevention and maintaining optimal health. There are about 30,000 genes in your body, and vitamin D affects nearly 3,000 of them, as well as vitamin D receptors located throughout your body.
According to one large-scale study, optimal Vitamin D levels can slash your risk of cancer by as much as 60 percent. Keeping your levels optimized can help prevent at least 16 different types of cancer, including pancreatic, lung, ovarian, prostate and skin cancers.
How Vitamin D Performance Testing Can Help Optimize Your Health
Is it any wonder then that no matter what disease or condition is investigated, vitamin D appears to play a crucial role? This is why I am so excited about the D*Action Project by GrassrootsHealth. Dr. Robert Heaney is the research director of GrassrootsHealth and is part of the design of the D*action Project as well as analysis of the research findings.
GrassrootsHealth shows how you can take action today on known science with a consensus of experts without waiting for institutional lethargy. It has shown how by combining the science of measurement (of vitamin D levels) with the personal choice of taking action and, the value of education about individual measures that one can truly be in charge of their own health.
In order to spread this health movement to more communities, the project needs your involvement. To participate, simply purchase the D*Action Measurement Kit and follow the registration instructions included. (Please note that 100 percent of the proceeds from the kits go to fund the research project. I do not charge a single dime as a distributor of the test kits.)
As a participant, you agree to test your vitamin D levels twice a year during a five-year study, and share your health status to demonstrate the public health impact of this nutrient. There is a $65 fee every six months for your sponsorship of this research project, which includes a test kit to be used at home, and electronic reports on your ongoing progress. You will get a follow up email every six months reminding you “it’s time for your next test and health survey.”
Internet Resources Where You Can Learn More
- Vitamin D for Public Health
- Free Vitamin D Educational Training for Medical Practitioners
- Scientific Consensus Paper Released; Assert Sunlight and Vitamin D are Essential for Human Health
- Vitamin D Resource Page
Where Do We Go From Here?
GrassrootsHealth is now undertaking a new project entitled the Protect our Children NOW! (POC) project. The aim of this project is to acquire participation of at least 500 pregnant women in a community, and to increase their serum levels to the suggested level of at least 40 ng/ml based on the clinical trial by Hollis & Wagner.
In addition, the project will take these results in two years and “march” on the various institutions in the state/government/to the March of Dimes, to demand that action be taken to protect the world’s next generation.
Among other items, the projects expected impact is likely to be a reduction in preterm births, (in some cases up to a 50 percent reduction). The project already has the blessing of the scientists, the physicians at the Medical University of South Carolina (which are implementing it in their practices) and even the insurance company.
Any community can implement this and make a difference for themselves and others. For further information contact Jen Aliano, Project Manager, at [email protected].
Sources and References
- 1 The Gerontological Society of America June 19, 2016
- 2 News-Medical July 27, 2016
- 3 Elle UK July 25, 2016
- 4 PHE July 21, 2016
- 5 Health Spectator July 22, 2016
- 6 The Guardian Oct. 30, 2013
- 7 BBC News July 21, 2016
- 8 Psych Central 1995-2016
- 9 AJGP Dec.2006
- 10 BBC News July 21, 2016
- 11 Nutrition Research January 2011
- 12 Vitamin D, The George Mateljan Foundation 2001-2016





