By Dr. Mercola
So you’re carrying some extra weight around, what’s the easiest and healthiest way to get rid of it? Many believe the answer lies in burning off more calories than you’re taking in, and while this theory sounds reasonable, the reality is more complex.
Many also believe that cutting fat from their diet is an essential step, but this too is a myth1 that may actually prevent you from achieving the weight loss you seek.
It’s important to realize that you cannot exercise your way out of a poor diet. Research2 shows exercise is largely ineffective for producing any significant amount of weight loss on its own.
Part of this is because while you certainly burn more calories when you exercise, you cannot burn off thousands of excess calories each day.
For example, to burn off the calories from a Snickers bar you’d have to walk about five miles, and to offset a one -soda-per-day habit, you have to walk one hour per day just to prevent additional weight gain…
The good news is, weight loss can be achieved by virtually everyone, once you understand a few core concepts. A successful weight loss plan can be broken down into three easy-to-remember components:3
- Exercise effectively and get regular movement
- Eat REAL food4,5
- Time your meals to optimize metabolic function
High-Intensity Workouts Are the Most Effective for Weight Loss
When it comes to weight loss, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) combined with intermittent fasting is the most effective combo I know of.
 The Sprout House Organ...
Buy New $9.80
(as of 09:15 UTC - Details)
The Sprout House Organ...
Buy New $9.80
(as of 09:15 UTC - Details)
According to the American College of Sports Medicine,6 HIIT workouts tend to burn anywhere from 6 to 15 percent more calories compared to other workouts, and intermittent fasting helps “reset” your body to start burning fat rather than sugar as its primary fuel.
When done together, they create a powerful synergy that effectively sheds body fat and promotes optimal metabolic function.
The human body evolved performing very high-intensity activities for brief periods of time, and this kind of activity appears to be part and parcel of our genotype. When recreating this ancestral activity, you have plenty of options these days.
For example, you can perform high-intensity exercises on an exercise bike or elliptical machine, or take the high-intensity route to strength training. To learn more, please see “Why High-Intensity Workouts Are Best for Weight Loss.”
What You Need to Know About Calories and Weight Loss
According to the calorie myth, in order to lose weight all you need to do is follow the equation of “eat less, move more.” But, while these statements may sound valid, it will not work unless you get certain details right.
 BUMBLE BEE Premium Ski...
Buy New $37.35 ($0.62 / Ounce)
(as of 11:10 UTC - Details)
BUMBLE BEE Premium Ski...
Buy New $37.35 ($0.62 / Ounce)
(as of 11:10 UTC - Details)
A key piece of information is that all calories are not created equal. You can eat more calories and lose weight, or eat fewer calories and still gain weight. Your weight is affected by the source of the calories, not just the number of calories. Zoe Harcombe’s book, The Obesity Epidemic, is one of the most comprehensive documents I’ve ever seen that exposes the flaws of this myth.
Research by Dr. Robert Lustig has also shredded this dogmatic belief, showing that not even calories from different kinds of sugar (such as glucose and fructose) are treated identically by your body.
Refined fructose is actually broken down very much like alcohol, damaging your liver and causing mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunction in the same way as ethanol and other toxins, whereas glucose does not wreak this kind of metabolic havoc.
According to Dr. Lustig, fructose is “isocaloric but not isometabolic.” What this means is that identical calorie counts from fructose or glucose, fructose and protein, or fructose and fat, will cause entirely different metabolic effects.
Cut Calories Wisely
So, when it comes to cutting calories, it’s important to discern which calories will promote health and which ones will sabotage it. Simply going on a low-cal diet in which you ditch calorie-rich fats and/or opt for artificially sweetened products is not going to do you any favors whatsoever. As recently noted in The New York Times:7
 So Delicious Dairy-Fre...
Buy New $17.11 ($0.09 / Ounce)
(as of 05:45 UTC - Details)
So Delicious Dairy-Fre...
Buy New $17.11 ($0.09 / Ounce)
(as of 05:45 UTC - Details)
“In recent years, a number of studies8 have cast doubt on the health benefits of the traditional low-fat diet, suggesting instead that eating more fat — with the exception of trans fats — and less sugar and refined carbohydrates might be better for overall health.”
Even if you do initially lose weight on a low-fat diet, you’re sacrificing your long-term health by promoting insulin resistance and related diseases for the simple reason that low-fat diets tend to be high in sugars instead. For example, a recent meta-review9 published in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings found that once you reach 18 percent of your daily calories from added sugar, there’s also a two-fold increase in metabolic harm that promotes pre-diabetes and diabetes.
More often than not, you’ll find that the weight comes off much easier when you eat more healthy fats and less non-vegetable carbohydrates (added sugars, processed fructose, and processed grains). If all of this sounds complicated, don’t fret; it’s actually quite easy to figure this out once you grasp and memorize the basics.
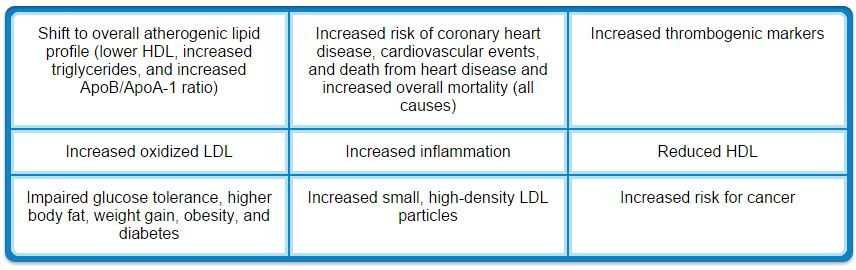
In a nutshell, all you really need to remember is that processed foods contain loads of ingredients that promote metabolic dysfunction, insulin resistance, and obesity, so the key is to eat REAL food. The following chart will provide a few more clarifying details:
Replacing Saturated Fat with Non-Vegetable Carbs Is a Recipe for Obesity and Poor Health
Most people have been indoctrinated to equate saturated fats with heart disease, but there’s really no evidence supporting this notion. On the contrary, an overwhelming amount of recent research has effectively dispelled this myth. Not only do saturated fats not promote heart disease, you actually need saturated fats for brain and immune system health.
Moreover, many vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble, and you have to have fat in order to absorb those vitamins from your food. Many also don’t realize that processed foods labeled as “low-fat” typically contain massive amounts of added sugars or artificial sweeteners instead. Start reading the labels and you’ll soon realize that the fat is simply traded for sugar, and that’s what’s really packing on the pounds…
Studies refuting the notion that saturated fats are bad for you include the following:
- A meta-analysis12,13,14,15 published in the British Medical Journal (BMJ), found no association between high levels of saturated fat in the diet and heart disease. Nor could they find an association between saturated fat consumption and other life-threatening diseases like stroke or type 2 diabetes. However, the study DID find a disease link to trans fatconsumption.
Trans fats were linked to a 28 percent increased risk for death from coronary heart disease, and a 34 percent increased risk of all-cause mortality. This is important because many “experts” frequently confuse trans fat with saturated fat intake.
- A pooled analysis of 11 studies16,17 showed that replacing saturated fat (found in foods like meat, egg yolks, dairy products, salmon, nuts, avocados, coconut oil, and olive oil) with monounsaturated fat (vegetable cooking oils),18 or carbohydrates (sugars and grains) raised the risk of non-fatal heart attacks. This prompted the authors to comment that dietary guidelines for saturated fats and trans fats “must carefully consider the effect of replacement nutrients.” This too is in line with previous findings, including this next one.
- In a 2014 editorial19 published in the Open Heart journal, research scientist and doctor of pharmacy James J. DiNicolantonio reviewed the cardiometabolic consequences of replacing saturated fats with carbohydrates, warning that the health consequences of doing so include:
Timing Your Meals Can Significantly Boost Weight Loss Success
There’s compelling evidence suggesting that when you eat morning, noon, and night, you increase your risk for both obesity and diabetes. Not only does this continuous grazing tend to lead to overeating in general, it also causes biological changes that result in metabolic dysfunction and subsequent weight gain and diminished health.
 Kirkland Signature Org...
Buy New $23.00 ($0.34 / Fl Oz)
(as of 02:45 UTC - Details)
Kirkland Signature Org...
Buy New $23.00 ($0.34 / Fl Oz)
(as of 02:45 UTC - Details)
Our ancestors did not have access to food 24/7, and from a historical perspective it appears your body was designed for intermittent periods of fasting. In fact, a number of beneficial effects take place when you go for periods of time without eating. For the last couple of years, I’ve suggested an intermittent fasting schedule that limits meals to a narrow window of six to eight hours a day — ideally by skipping breakfast, and having lunch be your first meal.
However, some people really struggle without breakfast, and I’ve more recently come to realize that you can skip breakfast ordinner — as long as you skip one of them. The key to remember is to only eat within a window of six to eight consecutive hours each day, and avoiding food for at least three hours before bedtime. However, due to the way your body generates energy from mitochondria production explained below, I am not convinced that it’s ideal to skip dinner. Another alternative is to have a very light meal as early as possible.
The Benefits of Avoiding Late-Night Eating
Eating too close to bedtime is another meal-timing factor that can sabotage your health. It’s important to have a minimum of three hours after your last food intake before you go to bed. Ideally, aim for as much as six hours between your last meal and your scheduled bedtime.
The rationale for this recommendation has to do with the way your body produces energy. Your mitochondria are responsible for “burning” the fuel your body consumes and converting it into usable energy. These tiny bacterial derivatives live inside your cell and are optimized to create energy from the food you eat and the oxygen in the air you breathe. Your cells have between 100 and 100,000 mitochondria.
Your mitochondria have a series of electron transport chains in which they pass electrons from the reduced form of the food you eat to combine it with oxygen from the air you breathe to form water. This process drives protons across the mitochondrial membrane, which recharges ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from ADP (adenosine diphosphate). ATP is the carrier of energy throughout your body.
A major side effect of this transfer of electrons is that some leak from the electron transport chain to react with oxygen to form the free radical superoxide. Superoxide anion, the product of a one electron reduction of oxygen, is the precursor of most reactive oxygen species and a mediator in oxidative chain reactions. These oxygen free radicals attack the lipids in your cell membranes, protein receptors, enzymes, and DNA that can prematurely kill your mitochondria.
Please understand that some free radicals are actually good and your body requires them to regulate cellular function. The problem is when you have excessive free radical production. Sadly that is the case for the majority of the population and why most diseases, especially cancers, are acquired. There are two possible solutions, increase your antioxidants or reduce mitochondrial free radical production.
I believe one of the best strategies for reducing mitochondrial free radical production is to limit the amount of fuel you feed your body when it requires the least amount, which is when you are sleeping. If you feed your body shortly before sleeping you will have large amounts of fuel your body simply has no need for, which will result in a massive increase in leakage of electrons that combine with oxygen to form free radicals, which damage your DNA, and thereby radically increases your risk of cancer.
This is one of the reasons why I rarely eat less than three hours before going to bed and frequently it is 5 to 6 hours. A review paper20 that provides much of the experimental work for the above explanation was published in 2011, titled “Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Animal Longevity: Insights from Comparative Studies.”
It may be too complex for many laypeople, but the take-home message is that since your body uses the least amount of calories when sleeping, you’ll want to avoid eating close to bedtime because adding excess fuel at this time will generate excessive free radicals that will damage your tissues, accelerate aging, and contribute to chronic disease.
Take-Home Message: to Normalize Your Weight, Eat Real Food, Exercise Wisely, Intermittently Fast, and Avoid Eating at Night
Focusing your diet on REAL FOOD rather than processed fare is one of the easiest ways to sidestep dietary pitfalls and myths that make weight loss difficult. Beyond that, it’s really just a matter of tweaking the ratios of fat, carbs, and protein to suit your individual situation. One key though is to trade refined sugar and processed fructose for healthy fat, as this will help optimize your insulin and leptin levels.
We’ve spent decades trading healthy saturated fats for carbs and trans fats, and there can be no doubt that this has had an enormous influence on disease statistics, raising incidence of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s — all the top killers. For more detailed dietary guidance, please see my optimal nutrition plan. It’s a step-by-step guide to feeding your family right, and I encourage you to read through it. I’ve also created my own “food pyramid,” based on nutritional science, which you can print out and share.
Sources and References
- 1 Authority Nutrition October 2015
- 2 Obesity June 2007: 15(6); 1496-1512
- 3 Business Insider August 11, 2015
- 4 Epoch Times October 19, 2015
- 5 New York Times October 19, 2015
- 6 American College of Sports Medicine, High Intensity Interval Training (PDF
- 7 New York Times September 23, 2015
- 8 New York Times September 2, 2014
- 9 Mayo Clinic Proceedings March 2015: 90(3); 372-381
- 10 Nutrition and Diabetes (2015) 5, e172
- 11 Nutritionfacts.org August 13, 2015
- 12, 16 BMJ 2015;351:h3978
- 13 Reuters August 12, 2015
- 14 Foodnavigator-usa.com August 12, 2015
- 15 Medical News Today August 12, 2015
- 17 American Journal of Clinical Nutrition February 11, 2009: 89(5); 1425-1432
- 18 Nutrition Data, Foods Highest in Monounsaturated Fat
- 19 Open Heart 2014;1: doi:10.1136/openhrt-2013-000032
- 20 Journal of Aging Research 2011 Article ID 807108